Measurement Equipment
- Different equipment is used to measure different values
- This includes the ...
- Stopwatch (Time): Measures time to the hundredth of a second between the pressing of the two consecutive stop/start button
- Thermometer (Temperature): Measures temperature in Celsius or Farenheit, mercury inside rises and falls in accordance to the temperature
- Balance (Mass): Measures the mass of the object by putting the object on top of the balance
- Burette (Volume): Graduated glass cylinder with levels of the liquid indicating the volume of the substance
- Pipette (Volume): Pipette (Volume): Glass tube with a bulge in the middle, and measures the volume of the substance
- Measuring Cylinder (Volume): Cylinder that measures the volume of a liquid
Criteria of Purity
Paper Chromatography
- Chromatography is a technique for separating chemical substances (mixtures of different components)
- The procedure for chromatography is...
- The tested substance(s) are absorbed by the paper on a drawn pencil line near the bottom of the strip of the paper
- The paper is clipped so that the paper (has to be below the pencil line) touches the water
- Observe the separating components, and you should have separate dots representing the different components of the original substance
- It works by...
- The components are carried by the water upwards
- Different components of chemical substances travel at different rates across paper
- Therefore, we can see the different components visually separated on the paper as each component will separate after moving at different rates across the paper

Diagram of Chromatography
Chromatograms and Rf Values
- The amount of spots in chromatogramsrepresents the number of components present
- The further a component travels up the paper, the more soluble it is
- If the ink does not move, that means it is insoluble
- Substances with one component (one spot) are pure
- Substances with more than own component are mixtures
- Rf (Retention factor) values represent how soluble a molecule is in the solvent
- The formula of the Rf value of a molecule is: distance travelled by component (the distance from the pencil line to the dot of the component) divided by the distance travelled by the solvent (the distance travelled from the pencil line to the end of the wet region of the paper)
- A high Rf value would indicate highly soluble substances that dissolve quickly into the solvent
- A low Rf value would indicate larger molecules that are harder to dissolve
- Components of identical Rf values would most likely indicate that the components are the same molecules
Diagram of Rf factor calculations
Importance of Purity
- Pure substances are defined as substances either made up of only one type of atom or molecule (eg. pure iron would be only made up of iron atoms)
- Pure substances have clear physical properties and predictable chemical properties
- Impurities may change these properties and start other reactions
- If substances such as drugs or food additives were not pure, they could have side effect
- Chemists also often use substances that are of high purity to conduct chemical experiments
Purity and Melting and Boiling Points
- Mixtures tend to melt and boil over a range of temperatures
- Pure substances tend to have a constant sharp melting and boiling point, meaning that it is rather specific and not a range
- Therefore, we can determine the purity of a substance based on how sharp their melting or boiling point is
- The smaller the range of the melting and boiling points, the purer the sample
Methods of Purification
Separation happens through taking advantage of some sort of difference between substances. These are some methods of purification which separate different mixtures
- Filtration
- Used to separate a liquid and insoluble solid
- When the mixture is poured on filter paper, the smaller molecules of the liquid will pass through while the larger solid will not and remain on the paper as residue
- Method
- Set up the experiment so that filter paper is placed inside of the filter funnel, which should be placed in the hole of a container such as the conical flask in the diagram
- Pour the mixture in the filter funnel
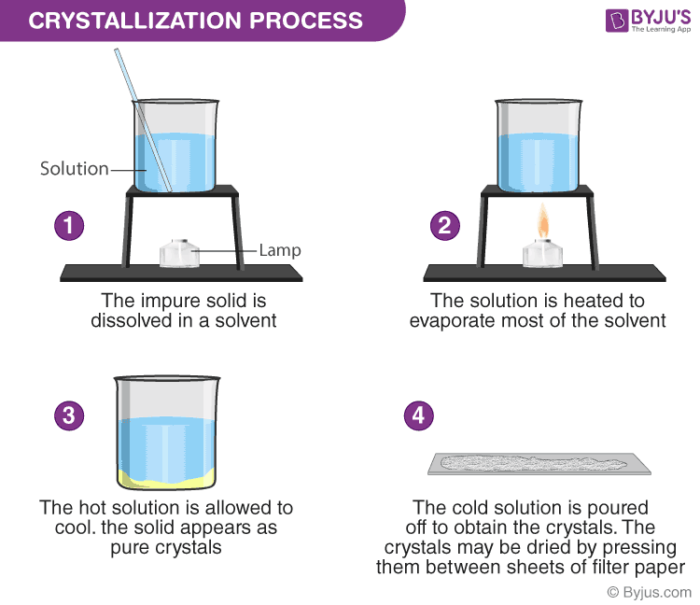
- Crystallisation
- Used to separate a solid that has been dissolved into a solution
- Method
- Heat the solution and wait for the solvent to evaporate
- Eventually, the maximum amount of solvent will be dissolved. This is called the saturated solution
- Dip a glass rod in the solution. When it is saturated, crystals will form on it
- The solid will become less soluble (less able to dissolved), and the crystals will therefore grow
- The crystals can be collected through filtration
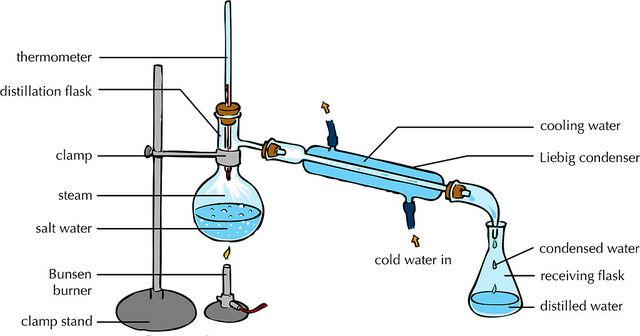
- Distillation
- Can separate the solvent and solute in a solution
- Can separate pure liquids from mixtures of liquids
- Method
- Heat the solution to evaporate the pure liquid into a vapour
- The vapour will condense in the condenser, cooling to turn back into a pure liquid in a beaker
- The rest of the mixture will be left behind and therefore separated in the flask containing the original mixture
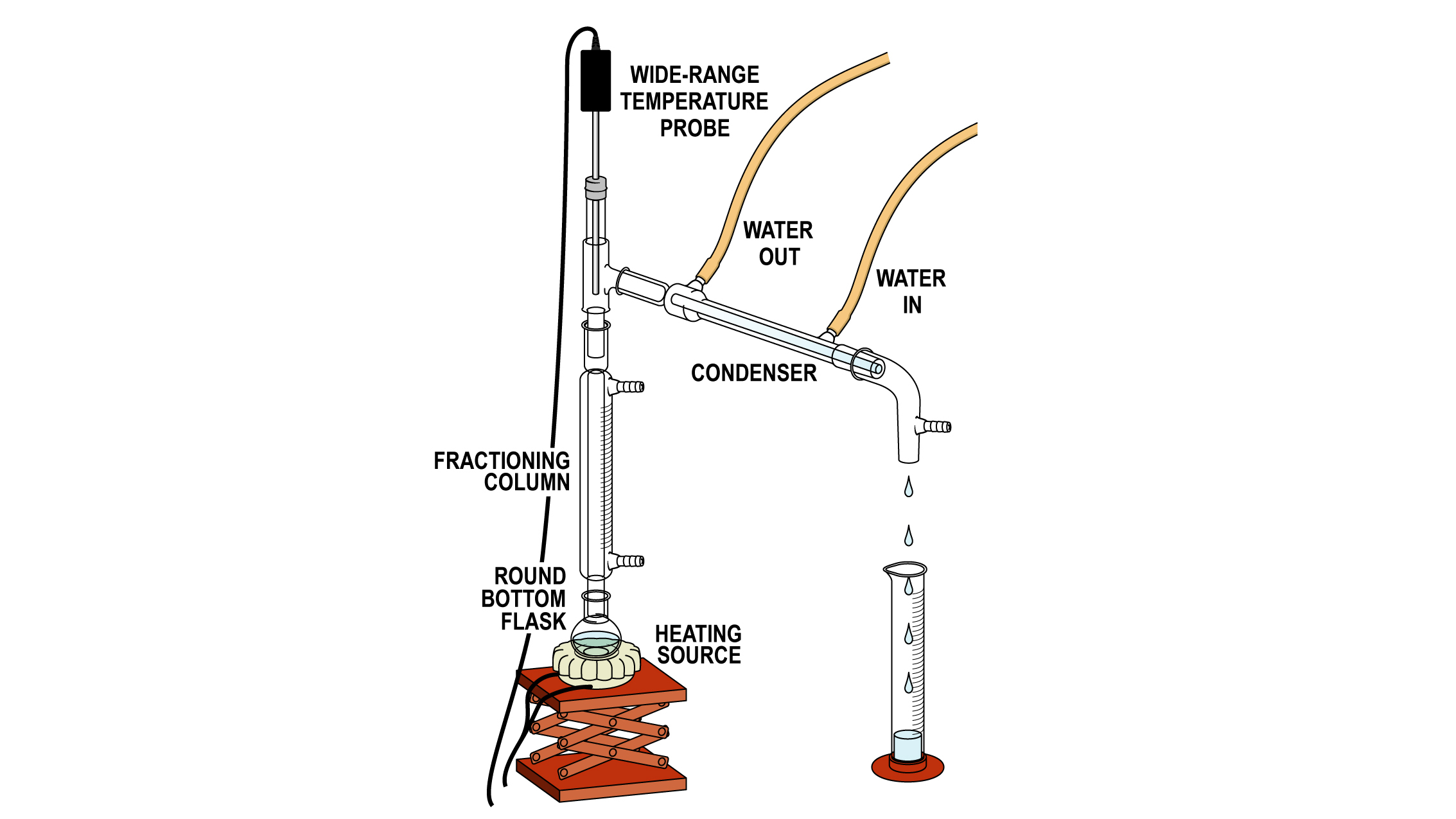
- Fractional Distillation
- Used to separate liquids that have been mixed together homogeneously
- Method
- Heat the solution to the boiling point of the liquid with the lowest boiling point to evaporate it into a vapour
- The vapour will condense in the condenser, cooling to turn back into a liquid in a beaker
- The rest of the mixture will be left behind and therefore separated in the flask containing the original mixture
↞Previous Topic Next Topic ↠
